Artwork Requirements
- Sending Artwork
- Raster vs Vector Graphics
- Acceptable File Formats
- Vectorization and Art Re-creation
- Logo Design
- PANTONE vs CMYK vs RGB
- Imprint Methods
Acceptable File Formats
- Vector Graphics Formats* Preferred
- Pixel Art Formats
Our in-house artists will review your artwork once it has been submitted to ensure the best possible print. If your art or logo require vectorization additional charges may apply.
Vector Graphics
Be sure to include any fonts or outline text in your files before sending. Vector graphics use geometrical primitives such as points, lines, curves, and shapes or polygon(s), which are all based on mathematical expressions, to represent images.
Vector File Formats*
- Adobe Illustrator [.ai, .eps, .pdf]
- Corel Draw [.eps]
- Inkscape [.svg]
* although these formats can contain vector art, they are capable of having pixel art embedded within them which may require art-recreation.
Pixel Art / Photographs
Pixel art can only be printed digitally and a minimum of 150 dpi and the exact size wanted on table cover, banner, etc. is required. Please note that many of our products require vector graphics for printing; if this is the case, vectorization charges may apply. Pixel art is a form of digital art, created through the use of raster graphics software, where images are edited on the pixel level. Photographs are an example of pixel art.
Pixel Art Formats
- Adobe Photoshop [.jpg, .png, .tiff, .bmp, .gif, .pdf]
Do not flatten layers; send original files with layers intact if possible.
Banner Artwork
Banner artwork that is not vector format needs to be at least150 dpi and the exact size of the banner (For an example, 33.5"W x 80"H). Please note that any graphics smaller than 150dpi will need to be either re-created with a possible art change or will be pixelated when printed.
Pixel Art Formats
- Adobe Photoshop [.jpg, .png, .tiff, .bmp, .gif, .pdf]
Do not flatten layers; send original files with layers intact if possible.
Sending Artwork
- If you are compressing your files, please do not send .sit or .sitx files. Instead compress them into a .zip or .7z using the free and open source 7-zip software.
- < 25MB: email to art@logoexpressions.com
- Up to 1GB: Upload Here (call 1-877-603-5646 for access)
- > 1GB: Send via dropbox, google drive, wetransfer, or other cloud storage service to the email address art@logoexpressions.com
- We also accept physical media (USB Drive, Hard Drive, CD-RW, zip disk etc.) however this method may result in delaying your order.
Raster vs Vector Art
Raster graphics are made up of thousands of pixels or dots and are limited to the Dots Per Inch (DPI) or Pixels Per Inch (PPI) that they were created in. Vector artwork is made up of mathematical curves and can be resized to any physical print size. Below is an example showing the difference between vector and raster graphics.
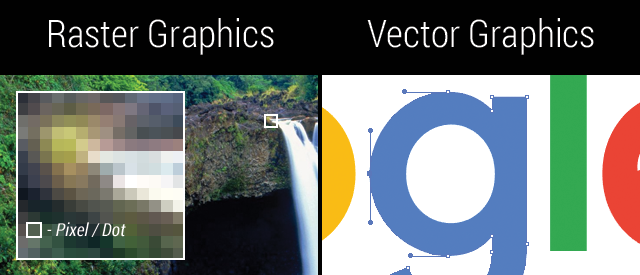
Vectorization and Art Re-creation
If your artwork requires vectorization/re-creation an additional charge may apply depending upon the complexity of your artwork.
This may apply to your art if:
Pros and Cons -- PANTONE vs CMYK Printing vs RGB display color
PANTONE
Pros
- Specific colors that are always consistent - no matter who prints them.
- Color vibrancy that is not possible with CMYK.
Cons
- You need to select your color from an actual printed swatch book because you cannot choose them via your pc screen.
CMYK
Pros
- Low cost printing in almost unlimited colors when printed digitally.
Cons
- Lack of color vibrancy -- Some colors will be much duller than what PANTONE offers.
- Cannot guarantee exact consistency of colors due to varying ink manufacturing methods.
RGB
RGB or HEX colors cannot actually be printed. If you absolutely must print an RGB graphic our printers will attempt to print the closest CMYK or Pantone color to the RGB values, however the colors cannot be matched exactly. Artwork created in RGB color mode can be converted with most professional graphics software packages to CMYK color and will attempt to replicate the color as closely as possible on screen, however as stated above in the PANTONE and CMYK sections, the only way to guarantee color replication is to choose and design with colors chosen from a PANTONE color book.
Imprint Methods
Dye-Sublimation
Uses heat to transfer dye onto medium materials such as a plastic card, paper, or fabric. The sublimation name is applied because the dye transitions between the solid and gas states without going through a liquid stage.
This method is not to be confused with dye sublimation heat transfer imprinting, which uses special inks to create transfers designed to be imprinted on polyester items.
Most dye-sublimation printers use CMYO (Cyan Magenta Yellow Overcoating) colors, which differs from the more recognized CMYK colors in that the black dye is eliminated in favour of a clear overcoating. This overcoating (which has numerous names depending on the manufacturer) is also stored on the ribbon and is effectively a thin laminate which protects the print from discoloration from UV light and the air, while also rendering the print water-resistant.
Heat Transfer
A method of imprinting a design or graphic on a product, such as a t-shirt, with the application of heat and pressure for a preset period of time. While heat presses are often used to apply designs to fabrics, they can also be used to imprint designs on table covers, mugs, plates, jigsaw puzzles, and other products.
Screen Printing / Silk Screening
A printing technique which uses a mesh is to transfer ink onto a product, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. This method of imprinting can be used for t-shirts, other apparel, posters, stickers, vinyl, wood, and other materials.
Embroidery
The process of decorating fabric or other materials with needle and thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as metal strips, pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. Embroidery is most often used on hats, coats, blankets, dress shirts, denim, stockings, and golf shirts. Embroidery is available with a wide variety of thread or yarn color.
Embossing / Debossing
An embossed pattern is raised against the background, while a debossed pattern is sunken into the surface of the material.
Laser Engraving / Laser Marking
The practice of using lasers to engrave a product. Laser marking, on the other hand, is a broader category of methods to leave marks on an object, which also includes color change due to chemical/molecular alteration, charring, foaming, melting, ablation, and more.
